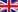
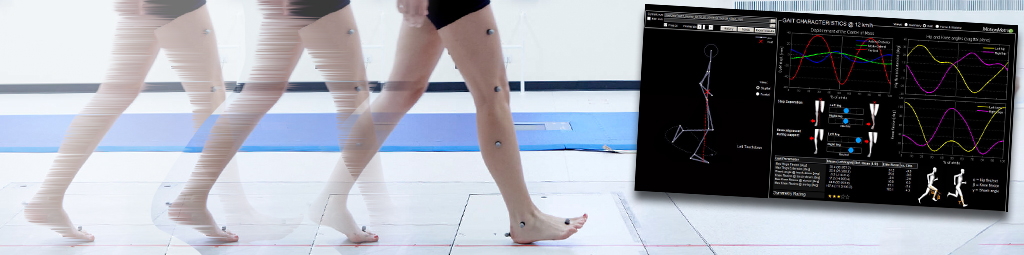
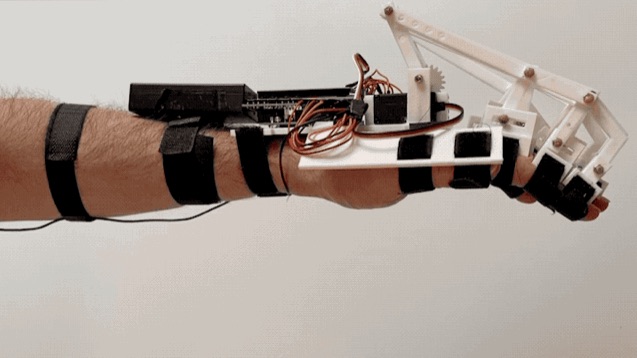
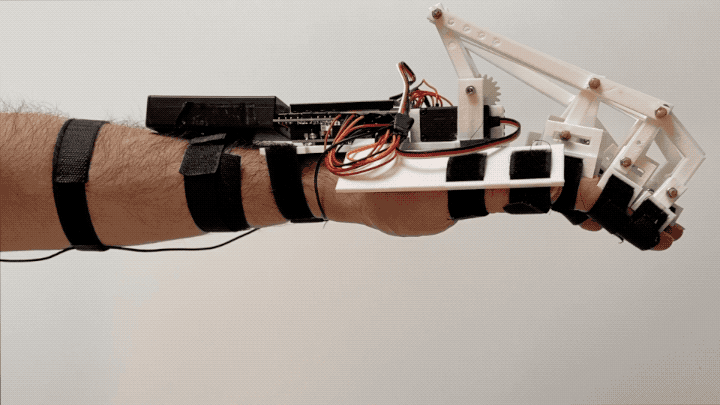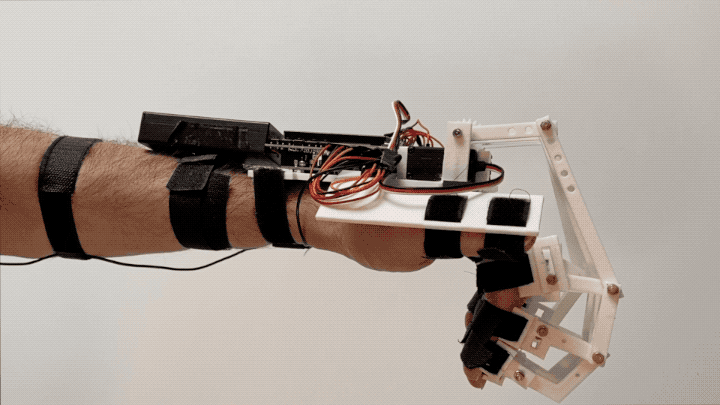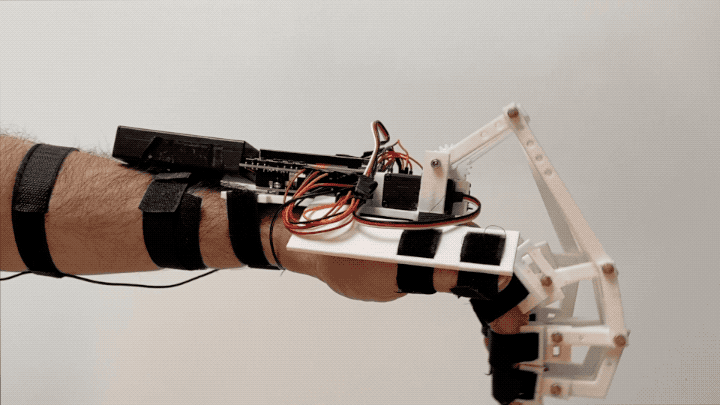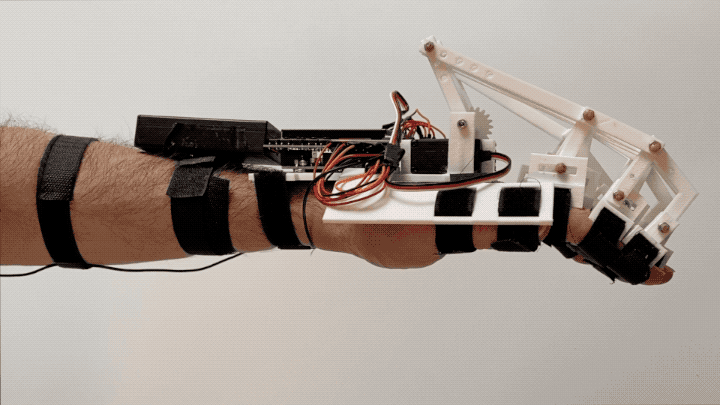
“Federica” hand is a low-cost, 3D printed prosthesis, able to perform the grasping function by using an underactuated mechanical system (a single off-the-shelf servomotor controls 15 phalanxes) [1,2,3,4]. The control system is based on a muscle sensor [5, 6] and an open-source Arduino platform [7,8], as alternative to the surface electromyography (sEMG).
“Federica” hand is a low-cost, 3D printed prosthesis, able to perform the grasping function by using an underactuated mechanical system (a single off-the-shelf servomotor controls 15 phalanxes) [1,2,3,4]. The control system is based on a muscle sensor [5, 6] and an open-source Arduino platform [7,8], as alternative to the surface electromyography (sEMG).
Various tests were carried out to verify the effectiveness of the “Federica” prosthetic hand in achieving simple daily life action (grabbing rigid and deformable objects; taking a bottle, a glass; catching a fly ball). The following video shows these tasks performed by a healthy subject.
Video test of the “Federica” hand prosthesis on a healty subject
If you are interested in the project and need informations about it, please leave your data in the contact form and we will try to answer you shortly.
Thank you for your interest in the "Federica" hand prothesis.
Open-Source Project: all the information to reproduce the “Federica” hand (including CAD files and software) can be downloaded from this link.
Bibliography
- Niola, V.; Rossi, C.; Savino, S.; Troncone, S. An underactuated mechanical hand: A first prototype. In Proceedings of the 2014 23rd International Conference on Robotics in Alpe-Adria-Danube Region (RAAD); 2014; pp. 1–6.
- Niola, V.; Rossi, C.; Savino, S.; Carbone, G.; Gasparetto, A.; Quaglia, G. An Underactuated Mechanical Hand Prosthesys by Iftomm Italy.; 2015.
- Bifulco, P.; Esposito, D.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Savino, S.; Niola, V.; Iuppariello, L.; Cesarelli, M. A stretchable, conductive rubber sensor to detect muscle contraction for prosthetic hand control. In Proceedings of the 2017 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB); 2017; pp. 173–176.
- Cosenza, C.; Niola, V.; Savino, S. A mechanical hand for prosthetic applications: multibody model and contact simulation. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2018, 232, 819–825, doi:10.1177/0954411918787548.
- Esposito, D.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Parajuli, N.; Cesarelli, G.; Andreozzi, E.; Bifulco, P. Measurement of muscle contraction timing for prosthesis control: a comparison between electromyography and force-myography. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA); 2020; pp. 1–6.
- Esposito, D.; Andreozzi, E.; Fratini, A.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Savino, S.; Niola, V.; Bifulco, P. A Piezoresistive Sensor to Measure Muscle Contraction and Mechanomyography. Sensors (Basel) 2018, 18, doi:10.3390/s18082553.
- Esposito, D.; Cosenza, C.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Andreozzi, E.; Niola, V.; Fratini, A.; D’Addio, G.; Bifulco, P. Experimental Study to Improve “Federica” Prosthetic Hand and Its Control System. In Proceedings of the XV Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing – MEDICON 2019; Henriques, J., Neves, N., de Carvalho, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 586–593.
- Esposito, D.; Savino, S.; Cosenza, C.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Fratini, A.; Cesarelli, G.; Bifulco, P. Study on the Activation Speed and the Energy Consumption of “Federica” Prosthetic Hand. In Proceedings of the XV Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing – MEDICON 2019; Henriques, J., Neves, N., de Carvalho, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 594–603.
- Esposito, D.; Savino, S.; Cosenza, C.; Andreozzi, E.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Polley, C.; Cesarelli, G.; D’Addio, G.; Bifulco, P. Evaluation of Grip Force and Energy Efficiency of the “Federica” Hand. Machines 2021, 9, 25, doi:10.3390/machines9020025.
- Esposito, D.; Savino, S.; Andreozzi, E.; Cosenza, C.; Niola, V.; Bifulco, P. The “Federica” Hand. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 128.
Other applications of Force Sensors:
- Andreozzi, E.; Fratini, A.; Esposito, D.; Naik, G.; Polley, C.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Bifulco, P. Forcecardiography: A Novel Technique to Measure Heart Mechanical Vibrations onto the Chest Wall. Sensors 2020, 20, 3885, doi:10.3390/s20143885.
- Andreozzi, E.; Centracchio, J.; Punzo, V.; Esposito, D.; Polley, C.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Bifulco, P. Respiration Monitoring via Forcecardiography Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 3996